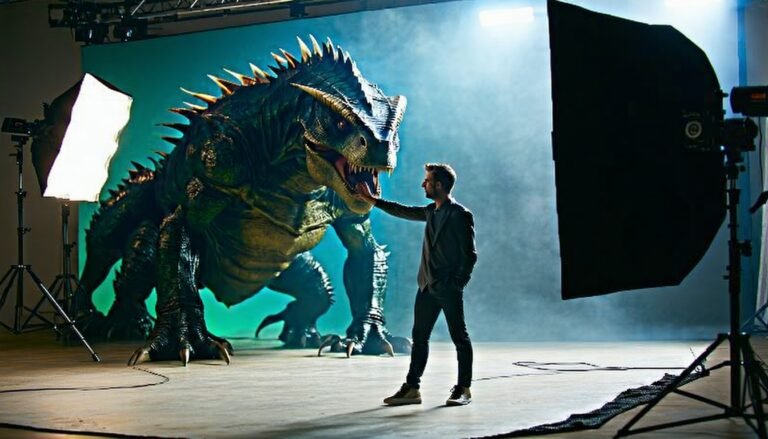
If you’ve ever marveled at giant robots stomping through city streets or dragons swooping over real actors, you’ve seen CGI/live action filmmaking in action. This craft seamlessly blends computer-generated imagery with on-set performances, making it difficult for viewers to distinguish between what is real and what is not. Ready to try it yourself? Let’s jump into an ultimate guide that walks you from concept to final polish.
Understand CGI/live action basics.
Let’s get the fundamentals down first. At its core, you’re combining digital 3D assets (like monsters, futuristic vehicles, or entire cities) with regular filmed footage. You’ll need to stay consistent with lighting, angles, and motion so both worlds look like they belong together.
Essential skills to cultivate
- 3D modeling, texturing, animation, and rendering.
- Live-action cinematography, including camera and lens knowledge.
- Compositing techniques for blending, color correction, and seamless transitions.
- A keen eye for detail, ensuring your CGI doesn’t “float” or stick out unnaturally.
Prepare your creative foundation.n
Pre-production is your sandbox for shaping the final look. By visualizing every shot ahead of time, you’ll spot potential pitfalls (like tricky lighting setups) before they ruin your day on set.
Plan your scenes
Storyboard each sequence so you know exactly when and where CGI elements will appear. Gather references, whether they’re real-world photos or concept art, to capture the look and scale you’re going for. This step helps you detect if, for instance, your 3D spaceship is too large compared to the actor’s vantage point.
Build or gather assets.
Create or source high-quality 3D models. If you’re making your own, keep polycounts manageable to avoid bogging down your machine. If you’re new to building 3D elements, consider exploring free libraries or starting with simple shapes, then layering in details.
Capture the right footage.
Your live-action footage is your baseline. Shoot in an environment that matches your planned CGI lighting style. If your digital creature emerges in broad daylight, film in bright conditions. If it’s a moody nighttime scene, match that on set.
Ensure consistent lighting.
Consider using tracking markers (stickers or crosses) to help you align CGI elements later. Keep your lighting kit consistent throughout the shoot so your CG additions won’t look pasted in. If you need advanced pointers, visit CGI/live action visual effects for more nuances on matching color and intensity.
Align and track 3D assets.
When your footage is ready, camera tracking is how you lock each CG element into the live-action space. The software analyzes points in the footage, calculating the camera’s movement so your 3D objects “stick” to the scene.
Match movement and perspective
If your actor walks around a corner, your CG character should pivot naturally in that 3D space, too. Reference your original storyboard for angles and depth. Always double-check the perspective in wide shots, as mismatches are more noticeable in these shots.
Compositing the final shot
Compositing is the magical step of blending all your layers—live action plates, CG elements, and effects like smoke or sparks—into a single image. This process can be as simple as layering two images or as elaborate as orchestrating dozens of elements.
Color correction and blending
Use consistent color profiles to ensure your CGI element doesn’t appear too warm or cool compared to the background. Tweak sharpness to match the camera’s depth of field. Don’t forget transitions. If you want to explore further, you can read about seamless CGI/live-action transitions and techniques for smoothing out edges where your CG meets the real world.
Polish in post-production
You’ve lined up the shots and composited everything, but there’s often more work to be done. This could include fine-tuning reflections, adding shadows, or correcting minor artifacts such as flicker or jagged edges.
Review and refine
Zoom in to check for any unnatural movement or color mismatch. Watch the final shot multiple times—preferably on a big screen. If you see any issues, adjust your layers accordingly. For in-depth guidance on post-production, visit CGI/Live Action Post-Production.
Review key takeaways
- Pre-production sets the stage, so storyboard every CGI shot for clarity.
- Matching lighting and angles ensures your CG object blends in seamlessly.
- Camera tracking pins digital elements to real movement.
- Compositing ensures that your final shot appears as one cohesive scene.
- Post-production fixes minor hiccups, allowing the audience to stay immersed in your story.
Mastering CG and live-action filmmaking is a learning process, and every new project sharpens your eye for realism. With the proper preparation, attention to detail, and a little patience, you’ll create visual magic that keeps viewers guessing which parts are genuine and which are digital. Good luck, and remember: if you can dream it, you can bring it to life on screen.
FAQS – Frequently Asked Questions
What is CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
CGI/Live Action Filmmaking combines computer-generated imagery with real-world footage to create seamless visual storytelling.
Why choose CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
CGI/Live Action Filmmaking allows you to blend fantastical elements with reality, expanding creative possibilities beyond practical filming limitations.
What are the main steps in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
CGI/Live Action Filmmaking typically involves pre-visualization, motion tracking, compositing, and final rendering to merge live footage and CGI.
Which software is used in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Popular tools include Maya, Blender, Nuke, After Effects, Houdini, and Premiere Pro for CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
Can filmmakers use CGI/Live Action Filmmaking on a budget?
Yes, CGI/Live Action Filmmaking can be accessible on a budget using open-source tools and creative workflows.
How does camera tracking fit into CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Camera tracking aligns virtual camera movement to real footage, ensuring CGI elements in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking stay properly positioned.
What role does green screen play in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Green screen footage allows for easy background replacement during compositing in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
How important is lighting in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Matching lighting between CGI and live footage is essential to avoid visual disconnects in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
Can you film practical sets and blend with CGI in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Absolutely; CGI/Live Action Filmmaking often starts with real sets enhanced by CGI for more dynamic visuals.
What is compositing in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Compositing merges CGI layers and live footage, balancing elements like color, shadow, and depth in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
How do audio and visual sync matter in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Perfect audio-visual sync ensures that CGI interactions align with live action, enhancing believability in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
Is motion capture used in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Yes—motion capture integrates realistic movement for CGI characters interacting with live sets in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
How does depth of field integrate in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
By matching camera lens settings and simulated focus blur, CGI/Live Action Filmmaking maintains visual coherence between elements.
Can CGI/Live Action Filmmaking fix errors in post-production?
Yes, visual elements such as removed objects or extended backgrounds can be seamlessly added during CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
What are common challenges in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Challenges include matching lighting, tracking accuracy, rendering speed, and achieving realistic interaction in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
How long does CGI/Live Action Filmmaking take?
Timelines vary—small shots take hours, while full sequences in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking can take weeks or months.
What training is needed for CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Training includes VFX courses, film production skills, understanding of lighting, tracking, and compositing for CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
Can real-time engines be used in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Yes, Unreal and Unity allow real-time previews and rendering for quick iterations in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
How do reflections and shadows work in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
By using HDRIs and ray-traced lights to simulate reflections and shadows that match live shot conditions in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking.
Are there career opportunities in CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
Yes—careers include VFX artist, compositor, technical director, and creative supervisor within CGI/Live Action Filmmaking teams.
What’s the future of CGI/Live Action Filmmaking?
The future of CGI/Live Action Filmmaking involves AI-driven workflows, virtual production, and increasingly photoreal interactive content.