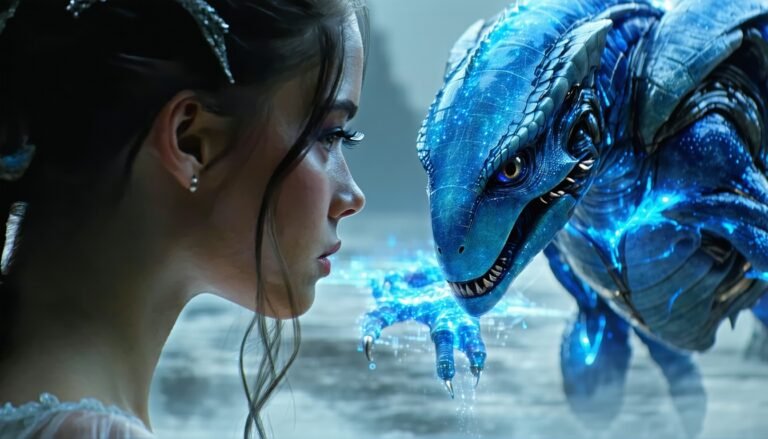
Have you ever watched a scene where computer-generated characters or environments blend so smoothly with real actors that you forget there’s any digital trickery involved? That’s the magic of seamless CGI and live-action transitions. You might be aiming to bring a massive alien cityscape to life behind human performers, or slip a photoreal creature into a filmed conversation. Whatever your goal, the process involves more than just fancy software. It’s about controlling every detail, from camera moves to color palettes, so the viewer’s eye can’t spot the difference between reality and CGI. Ready to see how it all comes together? Let’s explore the essentials.
Discover the fundamentals
Before combining CGI with live video, it’s helpful to understand the basics. CGI (computer-generated imagery) refers to any digitally created visual element, such as 3D models, special effects, or animated characters. Live action refers to raw, filmed footage captured on set or with a handheld camera. Bringing the two together is all about making it appear as though they’re part of the same world.
Why transitions matter
In many VFX (visual effects) projects, the biggest giveaway that something is “off” comes when the CGI element doesn’t match the real footage around it. Shadows, colors, or physics might be inconsistent. By nailing your transitions, you ensure a believable result that preserves the story you want to tell. After all, nobody wants their audience to pause and think, “Wait, that doesn’t look right.”
Core skills you’ll need
- Digital modeling and animation software (e.g., Blender or Maya)
- Knowledge of camera lens properties and perspective
- Lighting and rendering techniques
- Compositing skills (putting all elements together so they look natural)
If you’d like to brush up on behind-the-scenes workflows, you can explore our additional resources on CGI/live-action filmmaking.
Plan your shots carefully.
Pre-production is where you make the magic easier to achieve later. At this stage, you determine exactly which elements will be created using CGI and where they will appear in your live footage.
Storyboards and animatics
Sketch out or animate your scenes in rough form. This helps you figure out angles, movements, and timing. If you plan to superimpose a digital creature, your storyboard should show where that creature enters, what it does, and how it interacts with the environment.
Location and set considerations
Select a set or location that aligns with your visual objectives. Consider how the lighting will affect both your real actors and the CGI elements you plan to incorporate. If you’re placing digital objects behind actors, ensure the background is free of clutter that may distort or confuse your final image.
For insights on optimizing your filming location for post-production, you may find ‘CGI/Live Action Post-Production’ a handy reference.
Light and shoot effectively.
Once your plan is set, it’s time to capture the real footage. Your primary goal here is to achieve consistent lighting and camera movements, ensuring that your CG elements blend seamlessly with the live-action elements later on.
Matching lighting setups
When you add 3D models or digital characters, you’ll typically replicate the same direction and intensity of light in your 3D software. So, make sure to measure or document your on-set lighting angles, color temperature, and any environmental factors (such as bouncing light off walls).
Using tracking markers
If an actor or prop moves, or if the camera pans around, you’ll need tracking markers in the scene. These markers help your compositing and 3D software determine how objects are moving through the footage, allowing the CG element to match that motion perfectly. A few bright stickers on the wall or floor can save hours of guesswork when it’s time to align digital content.
Align CGI elements
Now comes the step where you integrate your CGI content with the real footage. First, you’ll build or animate your digital objects or characters in 3D software, ensuring their style and detail match the live scene.
Setting realistic materials
You’ll want to replicate the textures and finishes that exist in the real scene. Reflective surfaces, for instance, should believably mirror surrounding lights. If you’re placing a digital car on a city street, the car’s bodywork needs to catch light from streetlamps just as a real car would.
Rendering passes
To make compositing easier, it’s common to render multiple passes, including diffuse color, shadows, reflections, and so on. This layered approach gives you more control over how these elements blend into the final shot. When you’re fine-tuning the image, you can tweak the intensity of each layer individually.
Composite with finesse
Compositing involves placing your CG layers on top of or behind your live footage. Tools like Nuke or After Effects help you align, color-correct, and blend these layers to produce a single coherent scene.
Matching color and contrast
Subtle color differences can break the illusion instantly. If your CGI dinosaur looks slightly more yellowish than the surrounding environment, viewers notice. Use color matching and grading techniques to unify shadows, highlights, and mid-tones across the entire frame. For a deeper dive into compositing specifics, check out our guide on CGI and live-action compositing.
Masking and rotoscoping
Sometimes, you’ll want a digital object to appear behind a real actor. If that actor wasn’t filmed against a green screen, you might need to rotoscope, which is essentially drawing a precise outline around the subject so you can “slot” the CG behind them. This takes patience, but the final effect is well worth it.
Enhance the final look.
Even after your CGI and live action appear to mesh well, you can push the illusion further by adding small touches and post-production tweaks.
- Add atmospheric effects, such as fog, dust, or slight lens flares, to help visually tie your digital and real elements together.
- Layer in subtle reflections: You could show a digital character mirrored in a nearby window or a puddle of water.
- Include ambient details: Real life isn’t pristine, so a bit of noise, grain, or film texture can make your CG additions feel organic.
Our quick primer on CGI/live-action visual effects might inspire more ideas for those extra finishing touches.
Avoid common pitfalls
Even seasoned artists slip up sometimes. Steer clear of these frequent issues:
- Overly shiny or under-detailed CG models that don’t match the established reality
- Inconsistent shadows if you move lights or actors mid-shoot
- Unstable camera tracking leading to CG elements “sliding” across the scene
- Ignoring lens distortion so the CG object has a slightly different perspective than the real footage
Move forward with confidence
Seamlessly blending CGI and live footage isn’t always easy, but with careful pre-production, consistent lighting, and detail-oriented compositing, you can create stunning scenes that wow your audience. You’ve got this. Try each step methodically, refine your work, and don’t hesitate to iterate. The result will be a visual that sells every frame of your story without distracting the viewer.
Ready to sharpen your skills even more? You can revisit some of the connected topics, such as CGI/live-action filmmaking or CGI/live-action post-production, for next-level tips and techniques. Keep experimenting and learning, and soon, your transitions will look so realistic that nobody will be able to guess what’s truly CGI and what’s not.
FAQS – Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Seamless CGI/Live Action transitions refer to smooth visual edits where computer-generated imagery blends effortlessly into real footage without noticeable cuts or mismatches.
Why Use Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Using seamless CGI/Live Action transitions enhances immersion, maintaining continuity and visual coherence between digital effects and filmed scenes.
What Software Helps Create Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Tools like Nuke, After Effects, Fusion, and Premiere Pro are ideal for achieving seamless CGI/Live Action transitions through compositing and masking.
How Do You Match Lighting For Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
To achieve seamless CGI/Live Action transitions you must match color, shadows, and reflections between the CGI layers and live footage.
Can Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions Be Done in Real Time?
Yes, with real-time engines like Unreal Engine and Unity, you can preview and produce seamless CGI/Live Action transitions instantly.
What Is Match-Moving For Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Match-moving ensures camera movement in CGI aligns perfectly with live footage—critical for seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.
Do Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions Require Rotoscoping?
Often you’ll use rotoscoping to isolate subjects—essential for precise edges during seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.
What Role Does Depth Mapping Play in Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Depth mapping helps integrate foreground and background elements for seamless CGI/Live Action transitions by preserving spatial relations.
How Do You Maintain Continuity in Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Consistent lighting, motion blur, and color grade are all vital when crafting seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.
What Are Common Pitfalls in Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Pitfalls include mismatched lens distortion, incorrect scale, jittery tracking, and inconsistent grading during seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.
Can Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions Be Used on a Budget?
Yes—free tools like Blender and DaVinci Resolve still allow you to create seamless CGI/Live Action transitions with careful planning.
Are Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions Used in Films?
Absolutely—seamless CGI/Live Action transitions are widely used in feature films, commercials, and TV to elevate storytelling.
How Do You Blend Sound With Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Audio transitions—like matched reverb or ambient sound—help smooth the visual shift during seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.
What Is the Role of Motion Blur in Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Applying motion blur properly helps CGI elements feel part of live footage, critical for seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.
Can Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions Be Used in VR?
Yes, seamless CGI/Live Action transitions are beneficial in VR, maintaining immersion by avoiding jarring visual changes.
How Do Color Grades Affect Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Matching LUTs and color profiles is essential to achieve seamless CGI/Live Action transitions that feel natural.
What Tests Should You Run for Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Run frame-by-frame checks, edge bleed tests, and light match tests to ensure seamless CGI/Live Action transitions are invisible to viewers.
Do Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions Require High-End Hardware?
While helpful, seamless CGI/Live Action transitions can be achieved on mid-range machines with optimized settings.
Can AI Assist Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Yes, AI tools can help with rotoscoping, tracking, and matching tones—improving workflow for seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.
How Long Do Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions Take?
Time depends on shot complexity—simple transitions may take hours, while high-end effects might need days.
What Eye-Tracking Considerations Affect Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Smooth motion paths are essential—avoid sudden jumps in CGI elements to maintain seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.
Where Can I Learn Seamless CGI/Live Action Transitions?
Online courses, VFX academies, and software-specific workshops offer lessons on seamless CGI/Live Action transitions.