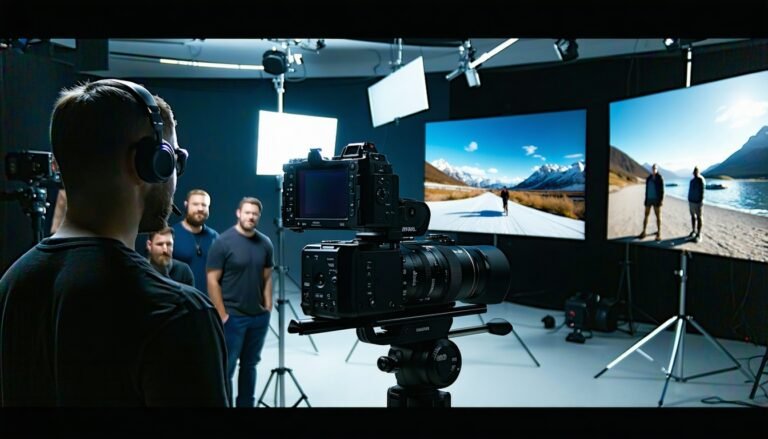
If you’re determined to create jaw-dropping visuals with genuine depth, advanced stereoscopic filmmaking can provide you with that immersive edge. It involves capturing separate images for each eye, then combining them to produce a 3D effect that draws viewers deeper into your story. While it may feel challenging at first, a focused approach will help clarify much of the complexity. Below, you will find a comprehensive guide to help you master stereoscopic projects from initial setup to final polish.
Discover stereoscopic fundamentals
Stereoscopic imaging begins with understanding a simple principle: each eye sees the same object from slightly different perspectives, creating the illusion of depth. In filmmaking, this is replicated by aligning two cameras (or using specialized stereoscopic rigs) to mimic the left-eye and right-eye viewpoints.
- Ensure your cameras or rig match in terms of resolution, frame rate, and color clarity. Differences can cause jarring mismatches.
- Keep each camera properly leveled to avoid excessive vertical offset. A slight tilt can introduce unwanted strain.
- When you begin your actual footage work, consider how various 3D depth creation techniques can help you push dimensional realism further.
Set up your cameras precisely.
When you set up a stereoscopic rig, the distance between the two lenses (known as the interaxial distance) largely determines how intense your 3D effect will be. Get it right, and you will wow your audience. Get it wrong, and viewers may feel cross-eyed.
- Start with a moderate interaxial distance, often around 2.5 inches (the approximate distance between human eyes).
- Test your rig in a controlled environment. Film a test subject at different distances to see how perspective shifts.
- Use markers or focus charts to confirm that both cameras are focusing similarly.
In specific productions, you might use sophisticated motors that dynamically adjust this distance based on the scene. Whatever your method, consistency is key so you do not introduce unnecessary viewer discomfort.
Enhance depth in post-production.n
After capturing your footage, post-production is where you can truly refine or alter the 3D illusion—many artists at this stage make extensive use of color correction, alignment adjustments, and depth enhancement.
- Sync your footage and align it carefully. Misalignment frequently causes severe eye strain.
- Use color correction to ensure uniform exposure, especially if one camera captured more light than the others.
- Explore layering and compositing techniques to enhance or reduce depth, aligning with your creative vision. If you plan to push the boundaries, also look into depth mapping in filmmaking for more complex transformations.
When adjusting 3D depth, consider referencing stereoscopic effects in movies that demonstrate how subtle changes in parallax can significantly impact audience immersion.
Address common pitfalls
Even top stereographers encounter problems specific to advanced stereoscopic filmmaking. Some of the most frequent culprits include:
- Ghosting: Overlaps between left and right images cause hazy outlines or double vision.
- Vertical misalignment: A slight angle difference between cameras can lead to headaches for your viewers.
- Convergence issues: If your point of convergence is too close or too far, the 3D effect may appear flat or uncomfortably strained.
When you spot these issues, address them promptly. A neat strategy could be to incorporate robust VFX for 3d movies that allow for digital tweaks in alignment or color. You might also want to fine-tune your interaxial distance in post if your rig supports that data.
Refine your final output.
Once your initial adjustments are complete, you can proceed to refine your final image. This is where professional touches help your stereoscopic film look smooth rather than gimmicky:
- Double-check edges and silhouettes. Is there any flickering or a residual halo around objects that appear too sharply?
- Perform a final pass on brightness and contrast to ensure both eyes receive consistent exposure.
- Screen your footage for friends or colleagues. Ask if they notice any anomalies, such as eye fatigue or subtle alignment errors.
Paying attention to these small details cements your reputation for precision and will keep your audience engaged without noticing the effect’s seams.
Plan your next steps.
As you become more comfortable with these processes, continue to explore ways to elevate your craft. Look for environments that push the boundaries of 3D, such as panoramic cityscapes or intricate close-up shots with strong foreground elements. Test different rigs, experiment with motion control systems, and study cinematic works that excel at using depth. Doing so will help you capitalize on advanced stereoscopic filmmaking for increasingly ambitious projects.
Ultimately, stereoscopy is about immersing your viewers in a convincing, vibrant three-dimensional universe. Every detail you refine, from lens pairing to final color grading, adds to that illusion of reality. With thoughtful setup, meticulous post-production, and a willingness to learn from any initial hiccups, you can craft unforgettable 3D experiences that showcase your growing expertise.
FAQS – Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Advanced stereoscopic filmmaking involves creating immersive 3D visuals by capturing and processing separate images for each eye, using sophisticated techniques and technologies.
How Does Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking Differ From Basic 3D?
Unlike basic 3D, advanced stereoscopic filmmaking uses precise camera alignment, depth grading, and post-production techniques to deliver more accurate and comfortable 3D experiences.
What Equipment Is Required For Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Advanced stereoscopic filmmaking requires dual-camera rigs, beam splitters, synchronized lenses, depth monitors, and high-end editing tools for precise control over 3D depth.
Why Is Depth Budget Important In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
In advanced stereoscopic filmmaking, managing the depth budget ensures comfortable 3D viewing by keeping objects within a safe convergence and divergence zone.
What Role Does Convergence Play In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Convergence in advanced stereoscopic filmmaking determines where the eyes naturally meet in the 3D scene, directly impacting audience comfort and depth perception.
Can Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking Be Used In Animation?
Yes, advanced stereoscopic filmmaking is widely applied in 3D animation to enhance spatial depth and visual immersion by rendering scenes from dual perspectives.
What Software Is Commonly Used In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Tools like Nuke, SGO Mistika, Adobe After Effects, and DaVinci Resolve are often used in advanced stereoscopic filmmaking to refine stereo effects and compositing.
How Are Live-Action Shots Handled In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Advanced stereoscopic filmmaking for live-action requires perfectly synced cameras and post-production alignment to ensure natural depth and eliminate eye strain.
Is Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking Suitable For VR?
Yes, advanced stereoscopic filmmaking is essential for VR as it creates realistic 3D depth, contributing to immersive and spatially aware virtual environments.
How Important Is Post-Production In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Post-production is critical in advanced stereoscopic filmmaking to adjust disparity, depth grading, and alignment for high-quality and comfortable 3D visuals.
What Are Common Challenges In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Advanced stereoscopic filmmaking faces challenges such as image alignment, depth mismanagement, parallax errors, and increased rendering and editing time.
Is Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking Used In Hollywood?
Yes, Hollywood films like Avatar and Gravity use advanced stereoscopic filmmaking techniques to deliver breathtaking and immersive 3D experiences.
Can Beginners Learn Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Beginners can learn advanced stereoscopic filmmaking through structured courses, practical training, and hands-on experience with stereoscopic cameras and software.
How Does Eye Strain Occur In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Improper convergence and excessive parallax in advanced stereoscopic filmmaking can lead to eye strain, emphasizing the need for precise planning and grading.
What Is Stereo Matching In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Stereo matching in advanced stereoscopic filmmaking ensures both eye images are aligned and consistent, preventing double vision and enhancing viewer comfort.
What Are Best Practices For Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Best practices include using calibrated rigs, maintaining a consistent depth budget, avoiding extreme parallax, and performing rigorous post-production review.
How Does Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking Impact Storytelling?
Advanced stereoscopic filmmaking enhances storytelling by adding spatial layers that guide viewer focus, intensify emotion, and increase engagement.
What Is The Future Of Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
With the rise of VR, AR, and 3D cinema, advanced stereoscopic filmmaking continues to evolve, pushing the boundaries of immersive storytelling and visual effects.
Are There Career Opportunities In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
Yes, professionals skilled in advanced stereoscopic filmmaking are in demand across film studios, VR companies, and animation houses globally.
Where Can I Study Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
You can study advanced stereoscopic filmmaking at specialized film schools, online platforms, or through workshops by industry professionals and studios.
How Is CGI Integrated In Advanced Stereoscopic Filmmaking?
CGI in advanced stereoscopic filmmaking is rendered from both left and right camera perspectives, ensuring perfect 3D integration with live-action footage.